A01
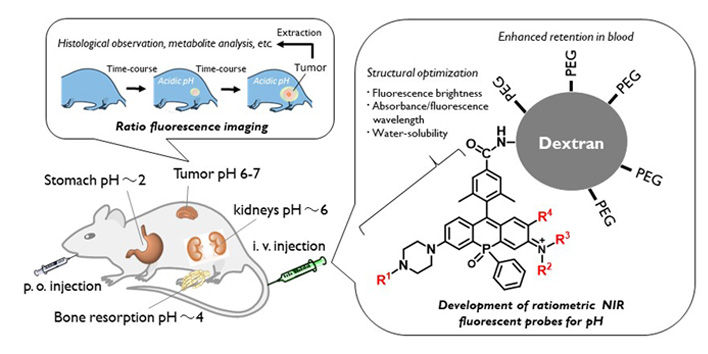
Development of fluorescent probes for visualizing the pH-based singularity inside bodies

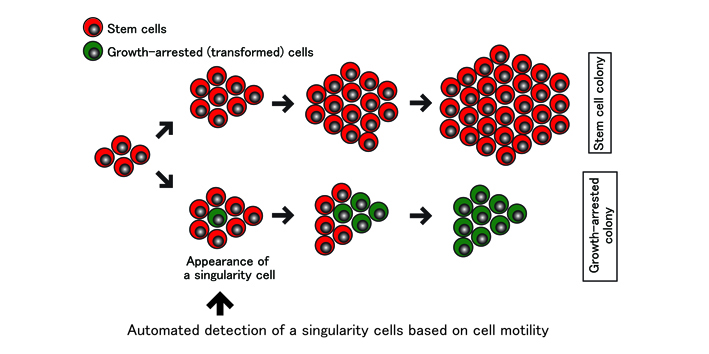
Development of the non-invasive method for detection of transformed cells in human stem cell cultures

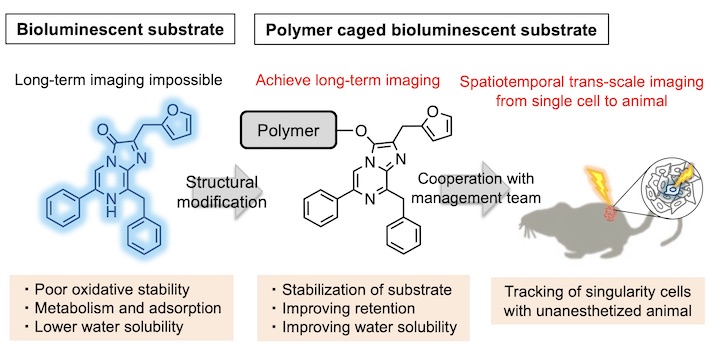
Development of polymer caged luciferin enabling spatiotemporal trans-scale imaging

Finding and Understanding Singularity Phenomena Using 4D Photoacoustic Imaging

| Name | Miya Ishihara |
| Affiliation | Dept. of Medical Engineering, National Defense Medical College |
| Major | Biomedical optical engineering |
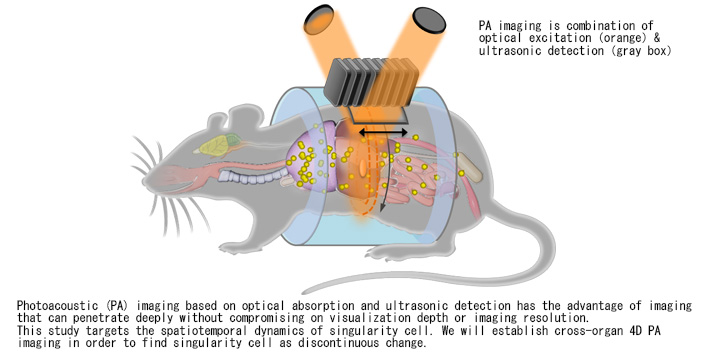
| Purpose | Photoacoustic (PA) imaging based on optical absorption and ultrasonic detection has the advantage of imaging that can penetrate deeply without compromising on visualization depth or imaging resolution. This study targets the spatiotemporal dynamics of singularity cell using PA imaging technology. We will establish cross-organ 4D PA spectroscopic imaging in order to find singularity cell as discontinuous change. |
A02
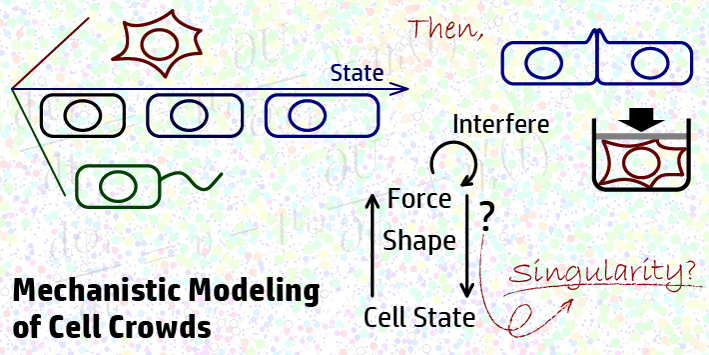
Mechanistic Modeling of Crowds Led by Cells of Singularity

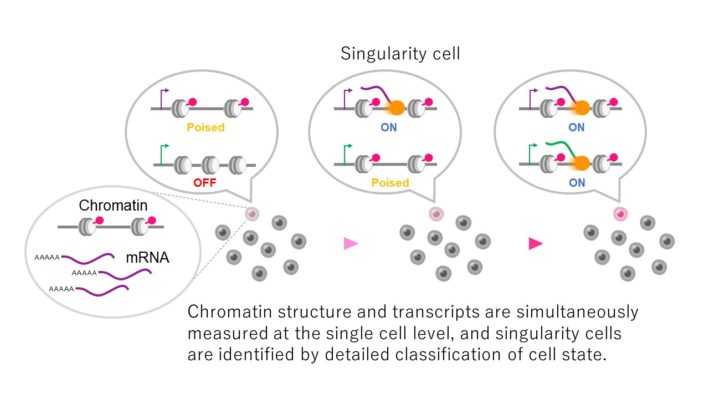
Development of single cell multi-omics tecnique for identification of singularity cells

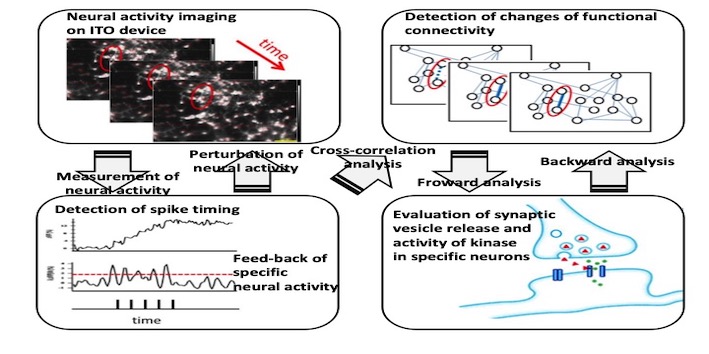
Detection of singularity neurons during neural network formation

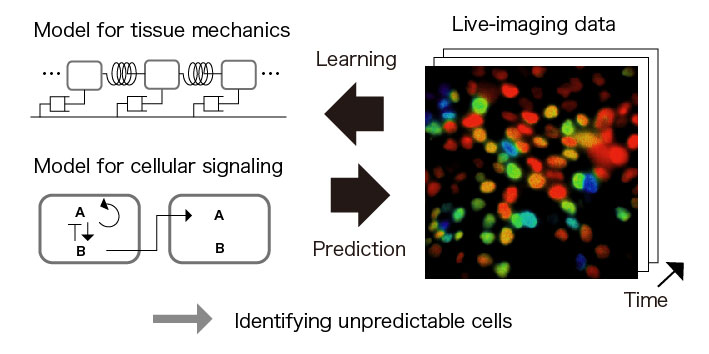
Identifying singular cells based on quantification of unpredictabiliy through spatio-temporal modeling

A03
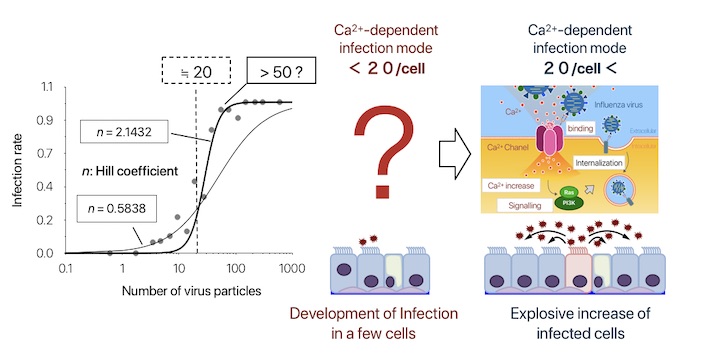
Singularity in influenza virus infection

Cancer-promoting singularity cells in pancreatic cancer

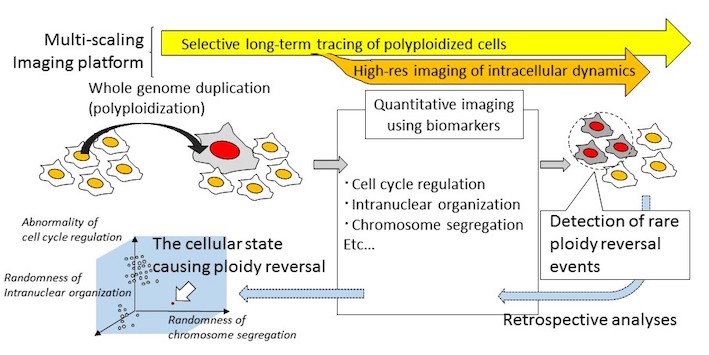
Elucidation of the principle of ploidy reversal in tumorigenesis

| Name | Ryota Uehara |
| Affiliation | Hokkaido University, Faculty of Advanced Life Science |
| Major | Cell Biology |
| Purpose | Whole genome duplication and subsequent chromosome loss (ploidy reversal), which drastically change cellular phenotypes, are hallmarks of cancer. However, as ploidy reversal happens at extremely low frequency both in cell cultures and tissues, it is difficult to specify cellular conditions that evoke the event and to trace its long-term consequences in the process of tumorigenesis. In this study, using a new imaging system that enables simultaneous high spatiotemporal imaging and long-term cell lineage tracing, we will identify rare cellular states that cause ploidy reversal and elucidate its principle and pathological contribution in tumorigenesis. |
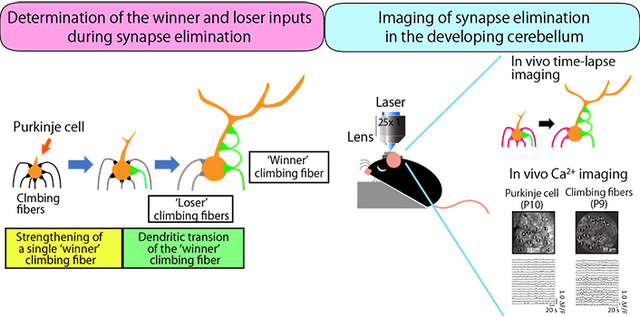
Imaging of synapse elimination in the developing brain

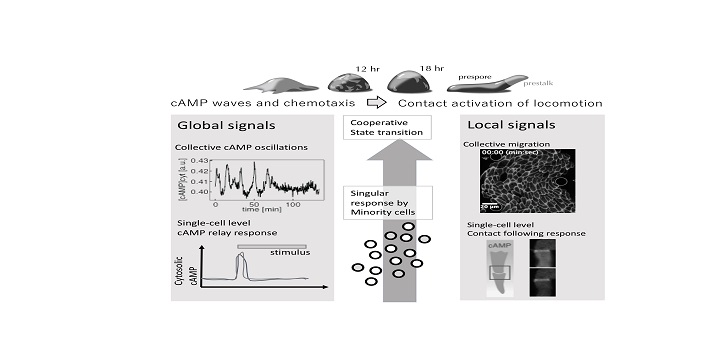
Singularity in the collectives state transition in Dictyostelium movement

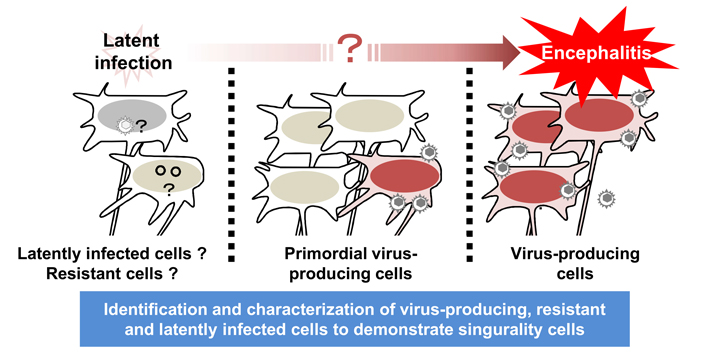
Life and death decisions on encephalitis

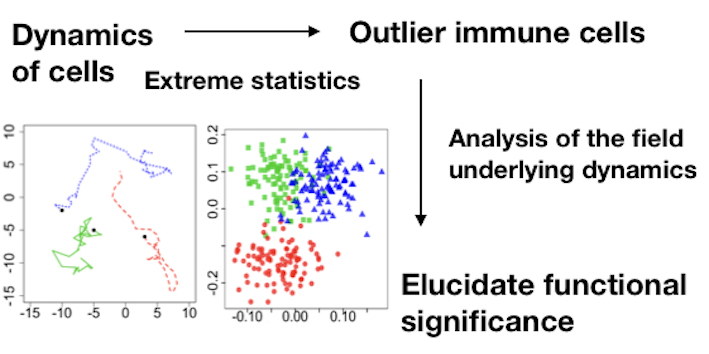
Mathematical modeling of outlier immune cells using extreme statistics

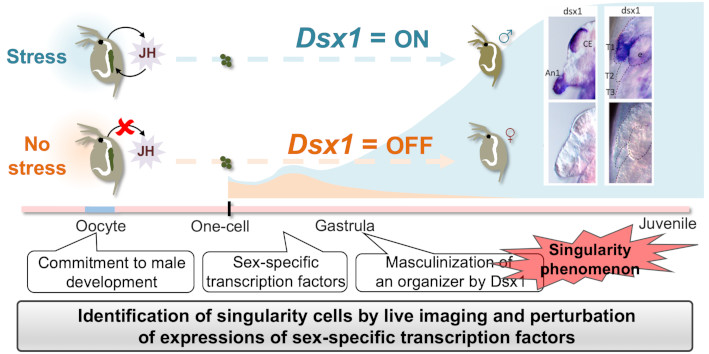
Identification of singularity cells that masculinize a primary organizer in response to environmental stimuli

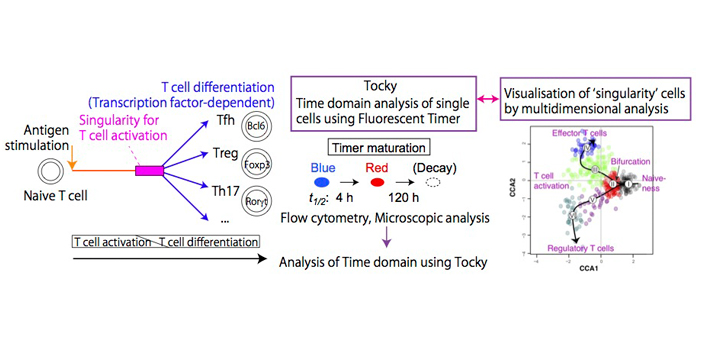
Elucidation of singularity events during immune reactions by Time-dependent Immunology and single cell analysis

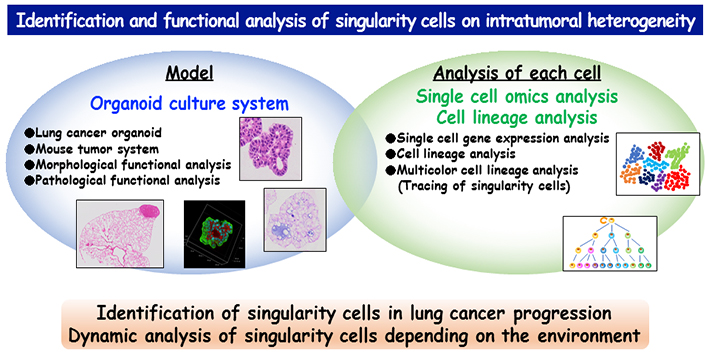
Identification and functional analysis of singularity cells on intratumoral heterogeneity

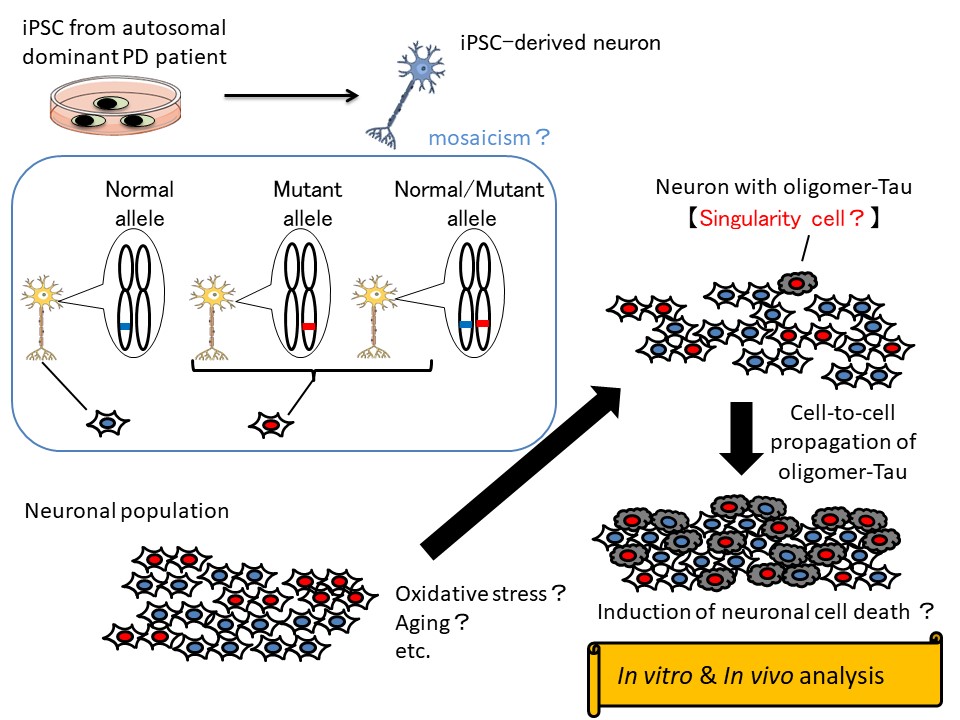
Analysis of the singularity phenomenon by mosaicism using disease-specific iPS cells

| Name | Etsuro Ohta |
| Affiliation | Kitasato University School of Allied Health Sciences |
| Major | Neuroscience |
| Purpose | Tau is related to cognitive dysfunction that is one of non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (PD). In this study, to elucidate the propagation of oligomer-Tau and its degradation mechanism by singularity phenomenon, we analyze disease-specific iPS cells (iPSC) from familial PD patient with LRRK2 mutation. Furthermore, to investigate whether singularity cells with oligomer-Tau are caused by mosaicism of mutant LRRK2 allele, we analyze iPSC-derived neurons under in vitro and in vivo conditions. |
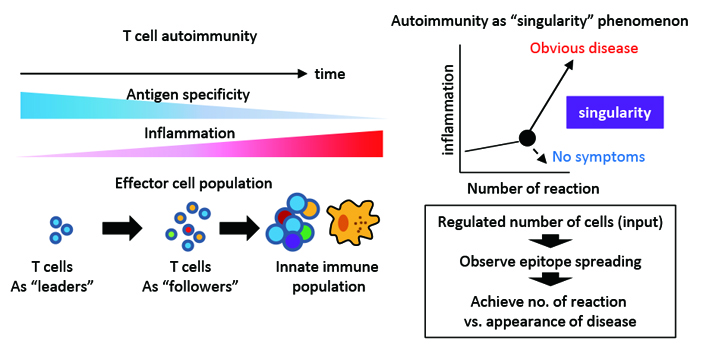
Singularity determining development of autoimmune diseases

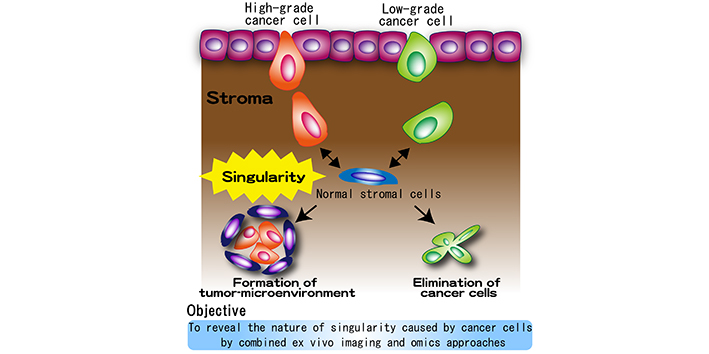
Evocation of singularity at emergence of cancer cells in normal stroma

| Name | Kon Shunsuke |
| Affiliation | Tokyo University of Science, Research Institute for Biomedical Sciences, Division of Development and Aging |
| Major | Cancer Biology |
| Purpose | Tumor microenvironment (TME) is a specialized, complex compartment comprising of tumor-educated stromal cells, which promotes both survival and proliferation of cancer cells. However, it remains enigmatic what happens at emergence of cancer cells in stroma, where normal stromal cells face to cancer cells at the first time. Our preliminary results suggest that normal stroma countervails the expansion of low-grade cancer cells, while high-grade cancer cells are able to transform normal storma into TME. In this study, we aim to reveal the nature of singularity at the initial stage of TME formation by combined ex vivo imaging and omics approaches. |
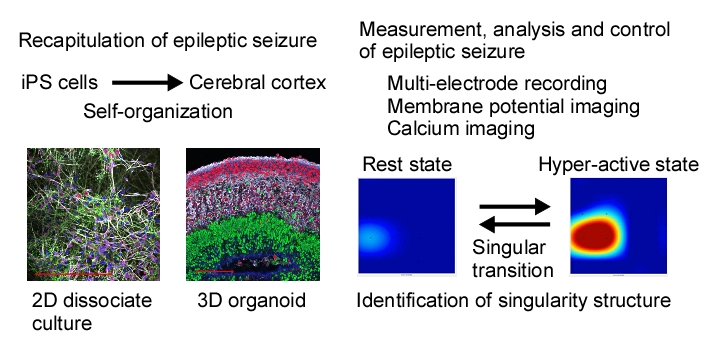
Analysis and control of singularity structures triggering epileptic seizure

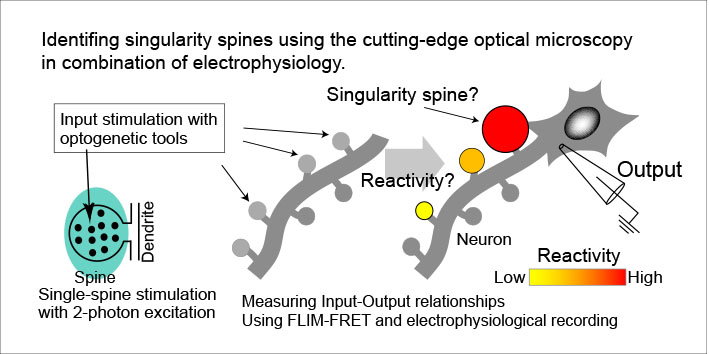
Search and functional analysis of singularity synapses

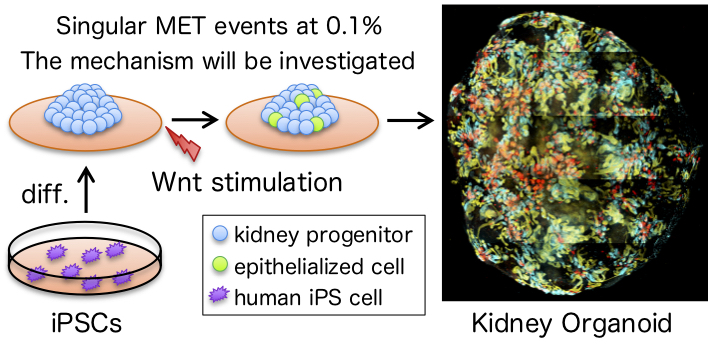
Investigation of emvironmental factors causing singular MET events using a realtime evaluation system

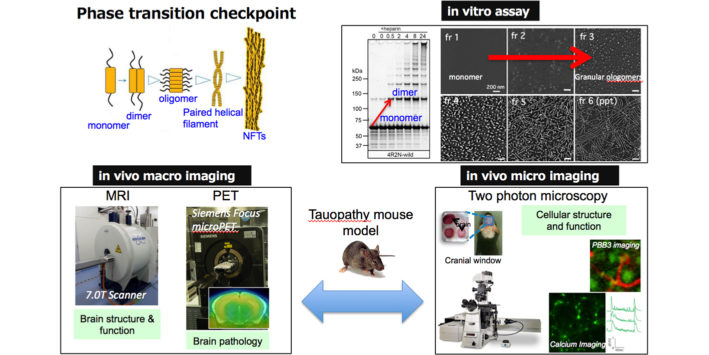
Investigating phase transition mechanisms of tau protein using in vivo multimodal imaging systems

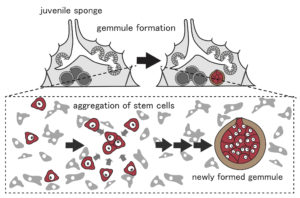
Regulatory mechanism of sponge stem cells